Creatine monohydrate is a widely used dietary supplement that has garnered significant attention in the realms of sports and fitness, as well as within the scientific research community. It is often regarded as one of the most effective and extensively studied supplements for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. This article is dedicated to providing a comprehensive exploration of creatine monohydrate, including what it is, how it works, and its effects on athletic performance, muscle building, and cognitive functions.
What is Creatine Monohydrate?
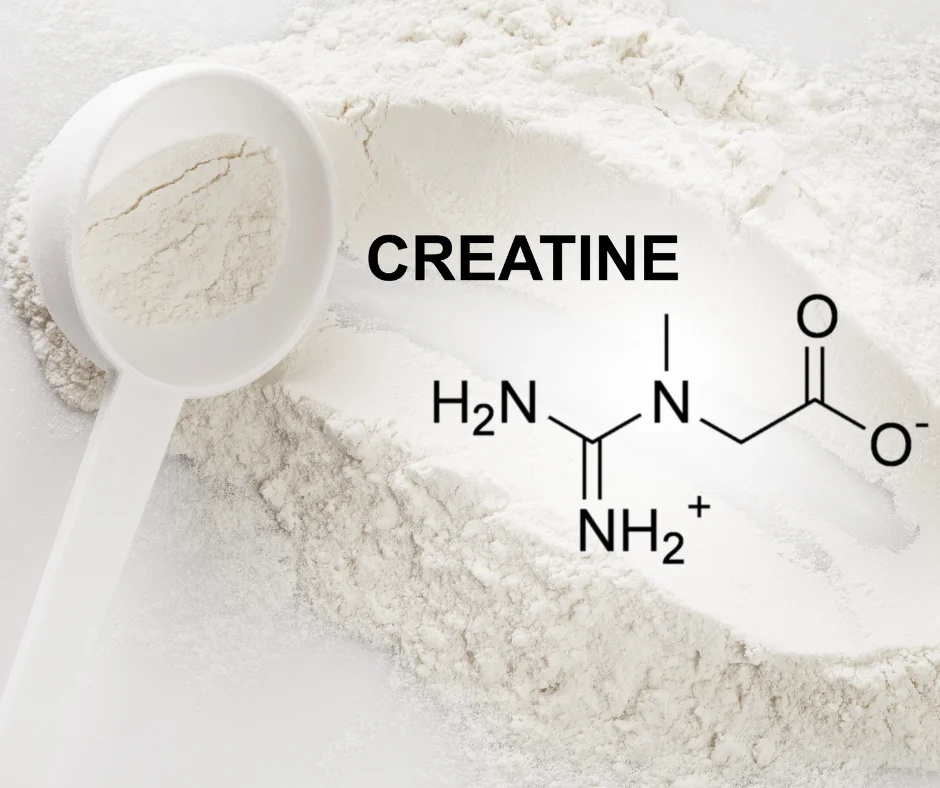
Creatine monohydrate is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in certain foods like red meat and fish. It plays a crucial role in the body’s energy metabolism, particularly in short-duration, high-intensity activities such as weightlifting, sprinting, and intense training.
In its supplement form, creatine monohydrate is commonly used to increase the body’s creatine stores in muscle tissue. It is one of the most stable and extensively researched forms of creatine and is often considered the gold standard.
How Does Creatine Monohydrate Work?
The mechanism of action of creatine monohydrate is based on its ability to enhance adenosine triphosphate (ATP) storage within muscles. ATP is the primary energy source for short-duration, high-intensity activities. For instance, when sprinting or lifting heavy weights, the body relies on ATP to sustain muscle contractions.
Creatine monohydrate increases the creatine phosphate stores within muscles, enabling rapid ATP regeneration. This allows the body to maintain higher performance levels for an extended duration before fatigue sets in.
Creatine Monohydrate and Athletic Performance
One of the most well-known and extensively researched effects of creatine monohydrate pertains to the enhancement of athletic performance. Numerous studies have demonstrated that supplementation with creatine monohydrate can significantly improve performance in activities involving high intensity and short duration.
This improvement can manifest in various sports, including:
- Strength Sports: Creatine monohydrate can assist in increasing muscle strength and performance in exercises like deadlifts, bench presses, and squats.
- Sprinting: Sprinters can benefit from enhanced sprint performance, as creatine monohydrate supports rapid ATP regeneration.
- Interval Training: Athletes engaged in interval training may experience faster recovery between bouts of exertion.
- Sports Involving Repeated Intense Efforts: This can encompass sports such as basketball, tennis, and rugby, where quick, explosive movements are crucial.
Creatine Monohydrate and Muscle Building
In addition to improving athletic performance, creatine monohydrate also has implications for muscle building. Supplementing with creatine can yield the following benefits:
- Increased Muscle Mass: Creatine monohydrate can promote cell volumization, leading to a temporary increase in muscle volume.
- Enhanced Protein Synthesis: Creatine may support the body’s ability to build muscle protein.
- Reduced Muscle Breakdown: Creatine can potentially slow down the breakdown of muscle tissue, especially during intense training sessions.
- Improved Training Quality: As creatine monohydrate can enhance performance, athletes can engage in more intense training sessions, completing more repetitions or lifting heavier weights.
Creatine Monohydrate and Cognitive Functions
Apart from its effects on physical performance, creatine monohydrate also has the potential to influence cognitive functions. Some research suggests that creatine may enhance cognitive functions, particularly those related to memory and mental sharpness.
This could be beneficial for individuals facing cognitive challenges, whether due to the aging process or certain neurological conditions.
Safety and Side Effects of Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is generally considered safe and well-tolerated when taken in appropriate amounts. Most people do not experience side effects from creatine, especially when adhering to recommended dosages.
However, some potential side effects could include:
- Stomach Discomfort: In some individuals, taking creatine monohydrate may lead to stomach discomfort.
- Weight Gain: Increased muscle mass and cell volumization can result in temporary weight gain.
- Fluid Retention: Some individuals may report mild fluid retention.
It’s important to note that most of these side effects are mild and transient. It is recommended to take creatine monohydrate in consultation with a physician or nutrition specialist, especially if there are any health concerns.
Dosage Recommendations and Usage
The recommended dosage of creatine monohydrate can vary depending on individual needs and goals. A typical loading phase involves consuming 20 grams of creatine monohydrate per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of approximately 3-5 grams per day.
It’s essential to stay adequately hydrated while taking creatine to minimize fluid retention and support kidney function.
Creatine monohydrate is a widely used dietary supplement with numerous potential benefits for athletic performance, muscle building, and cognitive functions. It has demonstrated safety and good tolerance when used within recommended dosages.
However, before using creatine monohydrate, it is advisable to consult with a physician or nutrition specialist to discuss your individual needs and goals. As with all dietary supplements, making an informed decision is crucial to achieve the best possible results.
[Include a comprehensive list of scientific studies, articles, and sources used in the article, properly formatted according to your preferred citation style.]